When building or upgrading a PC, choosing the right processor is crucial. Among Intel’s processor lineup, one key decision is choosing between K-series and non-K series CPUs. These two categories of Intel chips differ primarily in their performance capabilities, particularly overclocking, which directly impacts their suitability for various types of users ranging from casual consumers to enthusiasts and gamers.
In this article we are going to explore the differences between Intel K and non-K processors, helping you make an informed decision when selecting the best CPU for your needs.
What are Intel K and non-K processors?
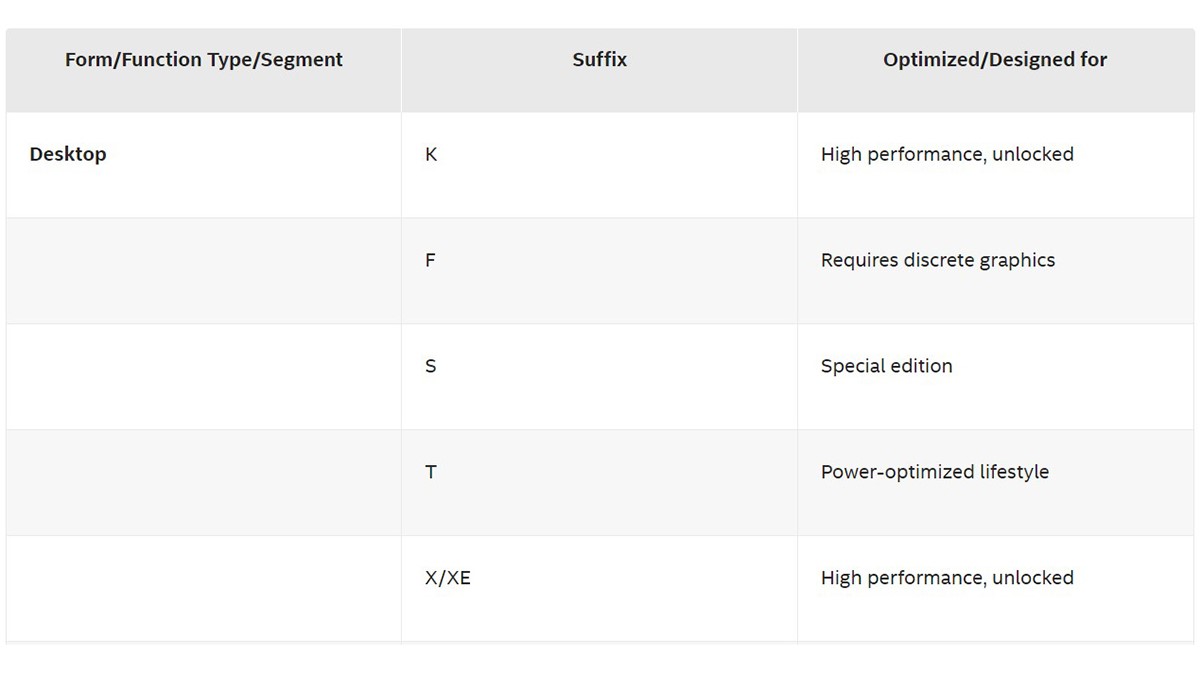
Intel offers a range of processors with different suffixes that indicate unique features. For instance, processors ending with a K (e.g., Intel Core i7-14700K) are unlocked, allowing users to fully overclock the CPU cores for increased performance. On the other hand, processors without the K suffix (e.g., Intel Core i7-14700) are locked, meaning the CPU cores are not intended for overclocking using standard methods; instead, they are designed to operate at their stock speeds.
Overclocking is essentially pushing a processor beyond its factory-set limits to achieve higher performance (see how to overclock your CPU), which is highly appealing to enthusiasts, gamers, and professionals who demand extra computing power. However, not everyone needs or benefits from overclocking, which is where non-K processors come into play.
Overclocking: The key distinction
The most significant difference between K and non-K Intel processors lies in overclocking. K-series processors are fully unlocked, meaning they allow users to adjust their clock speeds beyond the stock values, leading to higher performance in tasks like gaming, video editing, and other intensive applications. Overclocking is achieved by increasing the CPU’s multiplier, which raises the processor’s speed above its standard boost frequency, and manipulating other variables, like memory and fabric speeds.
Non-K processors, in contrast, are locked, preventing users from changing the clock multiplier for the CPU cores. Motherboard vendors have devised workarounds for some level of overclocking over the years, but these always fall short of the full overclocking potential of a K-series part. So, as a general rule, non-K CPUs run at fixed speeds, as defined by Intel, offering a more stable but less customizable performance profile.
For example, a Core i7-14700K processor can be overclocked to run at speeds higher than its boost 5.6-GHz frequency, depending on the quality of cooling and the motherboard used. Meanwhile, the Core i7-14700, its non-K counterpart, will run at its predefined maximum frequency without allowing users to push it further.
Older non-K series processors also won’t allow memory overclocking, but Intel recently enabled memory overclocking with locked chips on B-series motherboards.
Why overclocking matters
Overclocking is particularly valuable for the following users:
- Gamers: Higher CPU speeds can reduce frame rate drops and deliver smoother gaming experiences, particularly in CPU-bound games.Content creators: Overclocking accelerates tasks like video rendering, 3D modeling, and other CPU-heavy applications.
- PC enthusiasts: Overclockers enjoy fine-tuning their systems for the best possible performance, often using advanced cooling solutions to manage the heat generated by pushing hardware to its limits.
Not all users need this level of performance. For average users focused on general computing tasks such as web browsing, office work, or media consumption, the extra power from overclocking may go underutilized.
Core and Thread Count
Both K and non-K processors generally share the same number of cores and threads within a given generation and tier. For instance, the Core i7-14700K and Core i7-14700 both have 20 cores (8 performance cores and 12 efficiency cores) and 28 threads.
However, due to the K-series’ overclocking capabilities, the K variant will outperform its non-K counterpart when overclocking is enabled and optimized.
Base and Boost Clock Speeds
Another important distinction between K and non-K processors is their base and boost clock speeds. K-series processors typically ship with higher base and boost frequencies compared to their non-K counterparts. Even without overclocking, a K-series CPU might provide a slight edge in performance out of the box.
For example, the Intel Core i7-14700K has a base clock of 3.4 GHz and can boost up to 5.6GHz, while the Core i7-14700 operates at a base clock of 2.1 GHz and boosts to 5.4 GHz. Although the difference in maximum boost clock speeds may seem minimal, in scenarios where raw CPU speed matters (such as in gaming), this difference can translate into measurable performance gains.
Power consumption and Thermal Design Power (TDP)
With increased performance potential comes the need for greater power and cooling. K-series processors typically consume more power due to their overclocking capabilities and higher base/boost frequencies. They often have a higher TDP (Thermal Design Power), meaning they require more robust cooling solutions to maintain stable operation.
For example, the Core i7-14700K has a TDP of 125W, while the Core i7-14700 has a TDP of 65W. The higher TDP of K-series processors is a direct consequence of their ability to run at higher speeds and the extra power needed for overclocking. If you plan to build a system around a K-series CPU, you’ll need a capable cooler—air or liquid-based—to handle the extra heat generated, especially if you’re planning to overclock.
In contrast, non-K processors consume less power and generate less heat, making them suitable for quieter and more energy-efficient builds. Non-K CPUs are ideal for users who prioritize low power consumption and quiet operation over maximum performance.
Price differences
As you’d expect, K-series processors generally come at a premium due to their unlocked status and higher base performance. The ability to overclock and the slight increase in stock clock speeds contribute to the higher cost.
For instance, as of this writing, the Core i7-14700K retails for around $350, while the Core i7-14700 costs about $330. This price difference reflects the additional performance headroom and overclocking potential of the K-series chip. If you have a graphics card (see our list of best GPUs), you can also save money by purchasing a KF chip such as the 14700KF ($330), the same as the K SKU, except that it lacks integrated graphics.
If you don’t intend to overclock and are satisfied with stock performance, a non-K processor may offer better value for money, especially since it tends to consume less power and may not require an expensive cooling solution. Note that non-K CPUs may come with CPU coolers in the box, whereas K CPUs usually require you to buy your own, adding $20 to $200 to the price, depending on which cooler you buy.
On the other hand, the non-K model is hard to find in stock for some SKUs and may sometimes even cost more due to low inventory. For example, the Core i9-14900 costs $100 more than the Core i9-14900K. At press time, we couldn’t even find a Core i5-14600 (non-K) in stock anywhere, but the Core i5-14500 (non-K) was readily available for $239, while the Core i5-14600K was $269.
| CPU | Street Price (USD) | Cores | Base / Boost Clock | TDP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Core i5-14500 | $239 | 14 (6P / 8E) | 2.6 / 5 GHz | 65W |
| Core i5-14600 | out of stock | 14 (6P / 8E) | 2.7 / 5.2 GHz | 65W |
| Core i5-14600K | $269 | 14 (6P / 8E) | 3.5 / 5.3 GHz | 125W |
| Core i7-14700 | $329 | 20 (8P / 12E) | 2.1 / 5.4 GHz | 65W |
| Core i7-14700K | $351 | 20 (8P / 12E) | 3.4 / 5.6 GHz | 125W |
| Core i9-14900 | $578 | 24 (8P / 16E) | 2 / 5.8 GHz | 65W |
| Core i9-14900K | $468 | 24 (8P / 16E) | 3.2 / 6 GHz | 125W |
Motherboard requirements
To fully unlock the overclocking potential of a K-series processor, you need a compatible motherboard. Specifically, K-series processors require a Z-series chipset (such as the Z790 or Z690) to access the full overclocking features. These motherboards are typically more expensive than their lower-tier counterparts. They often come with additional features like improved VRMs (Voltage Regulator Modules) designs, better cooling, and support for higher memory frequencies.
On the other hand, non-K processors can run on more affordable chipsets like B-series (e.g., B760) or H-series (e.g., H770). While these chipsets don’t support overclocking the CPU cores, they support memory overclocking and provide more than enough functionality for everyday users and light gamers. The difference between the least expensive Z790 ($150) and a B760 motherboard ($90) was around $60 at press time.
If you’re building a system on a budget or simply don’t need overclocking features, opting for a non-K processor and pairing it with a mid-range motherboard can save you a significant amount of money.
Which one should you choose?
The choice between an Intel K and a non-K processor depends on your performance needs, budget, and whether you plan to overclock the CPU cores. K-series processors are the go-to for enthusiasts and gamers who want the freedom to tweak and extract maximum performance from their CPUs. In contrast, non-K processors are ideal for users who need solid, reliable performance without the need for additional complexity or cost.
When deciding between the two, consider factors such as your budget, cooling solution, motherboard options, and how much you value performance over energy efficiency and simplicity. For most users, a non-K processor will more than suffice, but if you’re the kind of user who wants to squeeze every last bit of power out of your system, the K-series is hard to beat. Just be prepared to spend $80 to $200 more on cooling and a motherboard.